Class 9 NCERT Solutions Biology Chapter 5: Fundamental Unit of Life
51
53
55
57
59
Fundamental Unit of Life Exercise 51
Solution 1
Robert Hooke discovered cells while examining a thin slice of cork under his self designed microscope. He observed that the cork resembled the structure of a honeycomb consisting of many little compartments, which he named cells. Cell in Latin means "a little room".
Concept insight: Most popular Exam question from this topic.
Solution 2
All living organisms are made up of cells. The number of cells in various living organisms varies greatly depending on the size of the organism. Many cells group together to form tissues, many tissues join together to form organ, many organs form organ system and finally all systems make up an organism, hence called structural unit of life.
A cell is able to live and perform the various functions of life. Each component in the cell carries out a specific function. In other words, it is a self-sufficient living entity. All the metabolic activities of life like respiration, digestion, excretion etc. occur at the cell level. So it is called the functional unit of life.
A cell is able to live and perform the various functions of life. Each component in the cell carries out a specific function. In other words, it is a self-sufficient living entity. All the metabolic activities of life like respiration, digestion, excretion etc. occur at the cell level. So it is called the functional unit of life.
Concept insight: Most popular Exam question from this topic.
Fundamental Unit of Life Exercise 53
Solution 1
Substances like CO2 move in and out of the cell by the process of diffusion. When the concentration of CO2 accumulates in the cell and is higher than the cell's external environment, it moves out and is thus excreted. Similarly, when its concentration is lower in the cell as compared to outside the cell, it moves into the cell.
Water also moves in and out of the cell by the same principle of difference of concentration, but the process through which water moves across a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis.
Water also moves in and out of the cell by the same principle of difference of concentration, but the process through which water moves across a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis.
Concept insight: Osmosis is a special type of diffusion in which movement of water takes place through semi permeable membrane whereas in diffusion movement of molecules takes place without a semi permeable membrane.
Solution 2
Plasma membrane allows only some selected substances to move in and out of the cell, and prevents the entry and exit of the other substances, so it is called a selectively permeable membrane.
Concept insight: Plasma membrane is also called as cell membrane. Students should not get confused between cell membrane and cell wall. Cell wall is not selectively permeable in nature.
Fundamental Unit of Life Exercise 55
Solution 1
Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
|
1. Size: generally small (1-10 1 |
1. Size: generally large (5-100 |
|
2. Nuclear region: Undefined nuclear region containing only nucleic acids is called a nucleoid. |
2. Nuclear region: Well defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane. |
| 3. Chromosome: single | 3. More than one chromosome. |
| 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles are absent. | 4. Membrane bound cell organelles (e.g., chloroplasts, golgi bodies, mitochondria etc.) are present. |
Concept insight:
- Differences should always be written in tabular form.
- Differences should be written in terms of their significance.
- Write only those many numbers of differences as stated in the question.
- Give example wherever possible.
Fundamental Unit of Life Exercise 57
Solution 1
Plastids and Mitochondria.
Concept insight: Apart form nucleus, plastids and mintochondria are the two cell orgenelles that contains their own genetic material and make some of their proteins. They are also called semi autonomous organelles.
Solution 2
Cell organelles are responsible for the organisation of a cell. Each cell organelle perform some specific function. If a few of these cell organelles are destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence , some of the important function of the cell will stop and it may result in the death of the cell.
Concept insight: Each cell acts as a single entity. Death of few cell components will result into the death of cell itself.
Solution 3
Lysosomes are known as suicide bags because whenever there is a disturbance in the cellular metabolism and the cell gets damaged or destroyed, the lysosomes burst and the powerful hydrolytic enzymes digest or eat their own cell. That is why they are called suicide bags.
Concept insight: Important from Exam point of view.
Solution 4
Proteins are synthesized in the ribosomes which are either attached to the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum or lying freely in the cytoplasm.
Concept insight: Important from Exam point of view.
Fundamental Unit of Life Exercise 59
Solution 1
The differences between plant cells and animal cells are as follows:
| Plant Cells | Animal Cells |
| 1.Plant cell are larger in size. 2.Cell wall is present. 3.Plastids (Chloroplast,chromoplast and leucoplast) are present. 4.Centrole is absent. 5.Larger vacuoles are present. 6.Food is stored in the form of starch. 7.Lysosomes are either absent or if present they are very few in number. 8.Golgi apparatus exist as small subunits called dictyosomes. |
1.Animal cells are comparatively smaller in size. 2.Cell wall is absent. 3.Plastids are absent. 4.Centriole with centrosome is present. 5.Vacuoles are either absent or if present they are very small in size. 6.Food is stored in the form of glycogen. 7.Lysosomes are present and are more in number. 8.Highly complex Golgi apparatus is present. |
Concept insight:
- Differences should always be written in tabular form.
- Differences should be written in terms of their significance.
- Write only those many numbers of differences as stated in the question.
- Give example wherever possible.
Solution 2
Difference between prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell are as under:
| Prokaryotic cell | Eurkaryotic Cell |
| 1.Generally small in size (1-10 m) 1m = 10-6m. 2.Undefined nuclear region containing only nucleic acids is called a nucleoid. 3.Single chromosome. 4.Membranne-bound cell organelles are absent. Example: Bacteria and blue green algae. |
1.Generally large in size(5-100 m). 2.Well defined nucleus surrounded by a Nuclear membrane. 3.More than one chromosome. 4.Membrane-bound cell organelles are present. Example: Plant cell and animal cell. |
Concept insight:
- Differences should be written in tabular form.
- Differences should be written in terms of their singnificance.
- Write only those many numbers of differences as stated in the question.
- Give example wherever possible.
Solution 3
Plasma membrane is the selectively permeable membrane that surrounds the cell and allows the entry and exit of selected materials into and out of the cell. If it ruptures, then
(i) The contents of the cell will come in direct contact with the outside medium and not only unwanted material will be able to enter freely into the cell, but useful material will also diffuse out of the cell.
(ii) The cell will lose its shape.
(i) The contents of the cell will come in direct contact with the outside medium and not only unwanted material will be able to enter freely into the cell, but useful material will also diffuse out of the cell.
(ii) The cell will lose its shape.
Concept insight: Plasma membrane is the outermost covering of both plant and animal cells protecting the inside material.
This question is important from Exam point of view.
Solution 4
Golgi apparatus helps in the packaging, storage and transport of substances in the cell. If there were no Golgi apparatus then the following things will happen:
(i) The material synthesised by Endoplasmic reticulum would not be carried to the various parts inside and outside the cell.
(ii) Synthesised materials could not be stored and modified further, as the Golgi apparatus performs the function of storage and modification.
(iii) There will be no production of lysosomes which will cause the accumulation of waste material, worn out and dead cell organelles within the cell which will ultimately lead to cell death.
(ii) Synthesised materials could not be stored and modified further, as the Golgi apparatus performs the function of storage and modification.
(iii) There will be no production of lysosomes which will cause the accumulation of waste material, worn out and dead cell organelles within the cell which will ultimately lead to cell death.
Concept insight: Important from Exam point of view.
Solution 5
Mitochondria is called the powerhouse of the cell as it produces energy by oxidizing the food and storing it in the form of ATP (Andenosine Tri phosphate), which is called the energy currency of the cell. This energy is later used for various activities by the cell.
Concept insight: Most popular Exam question from this topic.
Solution 6
The lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane are synthesised in the endoplasmic reticulum. Lipids are synthesised in the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) and the proteins are synthesised in the ribosomes attached to the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER).
Concept insight: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum are two different organelles. Ribosomes are attached only to the surface of rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Solution 7
Amoeba is a unicellular organism. It obtain its food through the false feet called pseudopodia. Whenever it sees food particle its flexible membrane protrudes and engulfs the food. This food is then broken down into the food vacuole which contains digestive enzymes. This process is known as endocytosis.
Concept insight: Most popular Exam question from this topic.
Solution 8
Movement of water molecules from the region of its higher concentration to the region of its lower concentration through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis.
It is a special type of diffusion.
It is a special type of diffusion.
Concept insight: Osmosis takes place through selectively permeable membrane only.
Solution 9
(i) Water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C because of the process of osmosis. The cell membrane of a potato is selectively permeable. As the cups B and C are filled with sugar and salt respectively and their outer part is in contact with the water, the concentration of water outside the cups is higher than inside the cups, so water moves from its higher concentration towards the lower concentration, i.e., inside the cup. This process of osmosis (moving in of the solvent) is known as endosmosis.
(ii) Potato A acts as a control for the experiment. It helps in comparing the result of the experiment.
(iii) Water does not gather in the hollowed out portion of A because there is no concentration difference and hence no osmosis takes place. Water also does not gather in the cup D as the cells of boiled potato are dead and hence no osmosis takes place.
(ii) Potato A acts as a control for the experiment. It helps in comparing the result of the experiment.
(iii) Water does not gather in the hollowed out portion of A because there is no concentration difference and hence no osmosis takes place. Water also does not gather in the cup D as the cells of boiled potato are dead and hence no osmosis takes place.
Concept insight:
(i) Follow the instructions properly.
(ii) Observe the activity carefully.
(iii) Give reason for your observation.
(i) Follow the instructions properly.
(ii) Observe the activity carefully.
(iii) Give reason for your observation.
Solution 10
For growth and repair mitotic division (mitosis) are involved as this type of division keep the chromosome number constant.
For gamete formation, meiosis is involved as reduction of chromosome number is necessary for this case.

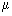 m)
m)