Class 10 NCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 10: Human Eye and The Colourful World
Human Eye and The Colourful World Exercise 164
Solution 1
When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and the distant objects are clearly visible to the eyes. To see the nearby objects clearly, the ciliary muscles contract making the eye lens thicker.
Thus, the focal length of the eye lens decreases and the nearby objects become visible to the eyes. Hence, the human eye lens is able to adjust its focal length to view both distant and nearby objects. This ability is called the power of accommodation of the eye.
Solution 2
The person is able to see nearby objects clearly, but he is unable to see objects beyond 1.2 m. This happens because the image of an object beyond 1.2 m is formed in front of the retina and not at the retina, as shown in the given figure.
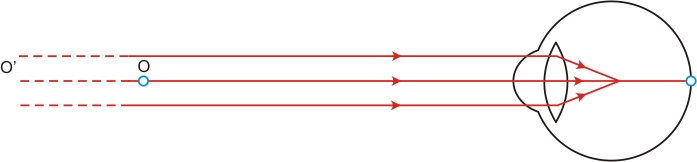
To correct this defect of vision, he must use a concave lens. The concave lens will bring the image back to the retina as shown in the given figure.
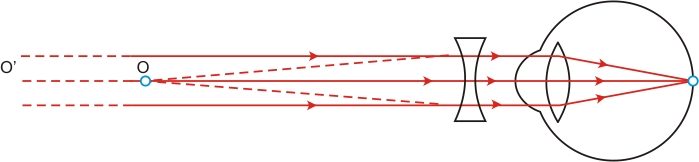
Solution 3
For human eye with normal vision, the far point is at infinity and near point is at 25 cm from the eye.
Solution 4
A student has difficulty in reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. It shows that he is unable to see distant objects clearly. He is suffering from myopia.
This defect can be corrected by using a concave lens.
Human Eye and The Colourful World Exercise Ex. 170
Solution 1
(b) accommodation
Concept Insight: Human eye can change the focal length of the eye lens to see the objects situated at various distances from the eye. This property of light is called accommodation.
Solution 2
(d) Retina
The human eye forms the image of an object at its retina.
Solution 3
(c) 25 cm
Concept Insight: The least distance of distinct vision is the minimum distance from the eye where an object can be seen clearly and distinctly. It is 25 cm for a young adult with normal vision.
Solution 4
(c) ciliary muscles
Concept Insight: The relaxation or contraction of ciliary muscles changes the curvature of the eye lens. The change in curvature of the eye lens changes the focal length of the eyes. Hence, the change in focal length of the eye lens is caused by the action of ciliary muscles.
Solution 5
The power P of a lens of focal length f is given by the relation
![]()
(i) Power of the lens used for correcting distant vision = -5.5 D
Focal length of the required lens, ![]()
![]()
The focal length of the lens for correcting distant vision is -0.181 m.
(ii) Power of the lens used for correcting near vision = +1.5 D
Focal length of the required lens, ![]()
![]()
The focal length of the lens for correcting near vision is 0.667 m.
Concept Insight: Concave lens is used for correcting short sightedness. Convex lens is used for correcting long sightedness.
Solution 6
Object distance, u = ∞
Image distance, v = -80 cm (at far point)
Focal length = f
According to the lens formula,
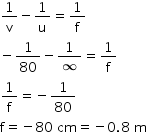
We know,
Power, ![]()
![]()
A concave lens of power -1.25 D is required by the person to correct his defect.
Concept Insight :80 cm distance corresponds to the distance at which the image of a far off object should be formed by the corrective lens, because that corresponds to the maximum distance at which if an object is placed, can be seen clearly.
Solution 7
A person suffering from hypermetropia can see distant objects clearly but faces difficulty in seeing nearby objects. It happens because the eye lens focuses the incoming rays from the object lying at normal near point beyond the retina. This defect of vision can be corrected by using a convex lens. A convex lens of suitable power converges the incoming light in such a way that the image is formed on the retina, as shown in the following figure.
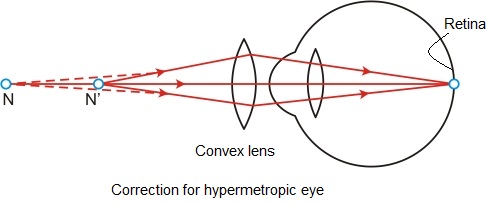
The rays starting from the normal ear point N' converge on passing through the convex lens, and appear to come from N, the near point of the hypermetropic eye.
Given:
Object distance, u = -d = -25 cm
Image distance, v = -1 m = -100 cm
Focal length, f = ?
Using the lens formula,
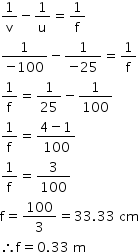
![]()
A convex lens of power +3.0 D is required to correct the defect.
Concept Insight: Concave lens is used for correcting short sightedness. Convex lens is used for correcting long sightedness.
Solution 8
A normal eye is unable to clearly see the objects placed closer than 25 cm because the ciliary muscles of eyes are unable to contract beyond a certain limit.
If the object is placed at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye, then the object appears blurred and produces strain in the eyes.
Solution 9
When we increase or decrease the distance of an object from the eye, the image distance in the eye (distance of retina from the eye lens) does not change. The increase in the object distance is compensated by the change in the focal length of the eye lens. The focal length of the eyes changes in such a way that the image is always formed at the retina of the eye.
Concept Insight: The property of the eye to be able to see the objects placed at different distances clearly is also known as accommodation.
Solution 10
Stars emit their own light and they twinkle due to the atmospheric refraction of light. Stars are very far away from the earth. Hence, they are considered as point sources of light. When the light coming from stars enters the earth's atmosphere, it gets refracted at different levels because of the variation in the air density at different levels of the atmosphere.
When the atmosphere refracts more star-light towards us, the star appears to be bright and when the atmosphere refracts less star-light, then the star appears to be dim. Therefore, it appears as if the stars are twinkling at night.
Concept Insight: Remember that twinkling of stars is just an illusion that appears due to the various atmospheric conditions.
Solution 11
Planets do not twinkle because they appear larger in size than the stars as they are relatively closer to Earth. Planets can be considered as a collection of a large number of point-size sources of light.
The different parts of these planets produce either brighter or dimmer effect in such a way that the average of brighter and dimmer effects is zero. Hence, planets not twinkle.
Concept Insight: One should remember the conditions that cause twinkling effect in stars while discussing about twinkling effect of planets.
Solution 12
The sky appears dark instead of blue to an astronaut because there is no atmosphere in the outer space that can scatter the sunlight. As the sunlight is not scattered, no scattered light reachs the eyes of the astronauts and the sky appears black to them.
Concept Insight: The prerequisite of the scattering process is the existence of particles of the size comparable to the wavelength of the light.
