Class 10 NCERT Solutions Biology Chapter 5: Life Processes
Life Processes Exercise 81
Solution 1
The body structure of multicellular organisms such as humans is very complex. They comprise of specialized cells and tissues for performing various important functions of the body. Unlike the unicellular organisms, multicellular organisms are not in direct contact with surrounding environment. Therefore, simple diffusion will not meet the oxygen requirement of all the cells and tissues.
Concept insight: Diffusion process should be clear.
Solution 2
Solution 3
a. Food for providing energy.
b. Oxygen for breakdown of food to obtain energy.
c. Water for proper digestion of food and other functions inside the body.
Concept insight: Remember the various raw materials required by a living organism for its survival.
Solution 4
a. Nutrition
b. Respiration
c. Excretion
d. Transportation
Concept insight: Students should know various types of life processes.
Life Processes Exercise 87
Solution 1
| Autotrophic Nutrition | Heterotrophic Nutrition |
| i. Food is synthesized from simple inorganic raw materials such as CO2 and water. | i. Food is obtained directly or indirectly from autotrophs. This food is broken down with the help of enzymes. |
| ii. Presence of green pigment (chlorophyll) is necessary. | ii. No pigment is required in this type of nutrition. |
| iii. Food is generally prepared during day time. | iii. Food can be prepared at all times. |
| Example: All green plants and some bacteria. | Example: All animals and fungi. |
Solution 2
(iii) Sunlight is absorbed by the chlorophyll and other green parts of the plant.
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Life Processes Exercise 91
Solution 1
Solution 2
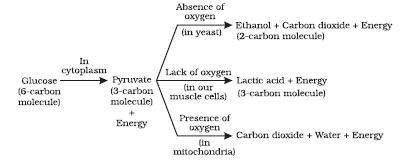
Solution 3
Solution 4
Life Processes Exercise 96
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
The plants take in water containing dissolved minerals from the soil through their roots. The roots of a plant have hairs called root hairs which absorb water and minerals from the soil. The root hairs are directly in contact with the film of water in-between the soil particles Water and dissolved minerals get into the root hairs by the process of diffusion. The water and minerals absorbed by the root hairs from the soil pass from cell to cell by osmosis through the epidermis, root cortex, endodermis and reach the root xylem.
The xylem vessels of the root of the plant are connected to the xylem vessels of its stem. So, the water containing dissolved minerals enters from the root xylem vessels into stem xylem vessels. The xylem vessels of the stem branch into the leaves of the plants. So, the water and minerals carried by the xylem vessels in the stem reach the leaves through the branched xylem vessels which enter from the petiole (stalk of the leaf) into each and every part of the leaf. In this way, the water and minerals from the soil reach through the root and stem to the leaves of the plant.
Solution 5
The transport of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation. The food made in leaves is loaded into the sieve tubes of phloem tissue by using energy from ATP. Water now enters into sieve tubes containing sugar by the process of osmosis due to which the pressure in the phloem tissue rises. This high pressure produced in the phloem tissue moves the food to all the parts of the plant having less pressure in their tissues. This allows the phloem to transport food according to the needs of the plant.
Life Processes Exercise 98
Solution 1
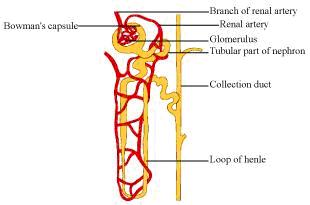
Solution 2
Solution 3
Life Processes Exercise 99
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
(d) The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll and sunlight.
Concept insight: Students should know the concept of autotrophic nutrition, organisms that carry out autotrophic mode of nutrition and raw materials required to carry out autotrophic nutrition.
Solution 4
(b) The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in mitochondria.
Concept insight:
Student should remember the process of aerobic respiration.
Solution 5
Fats are present in the form of large globules in the small intestine. The small intestine gets the secretions in the form of bile juice and pancreatic juice respectively from the liver and the pancreas. The bile salts (from the liver) break down the large fat globules into smaller globules so that the pancreatic enzymes can easily act on them. Lipase enzyme present in the pancreatic juice causes breakdown of emulsified fats. Glands present in the wall of small intestine secrete intestinal juice which contains lipase enzyme that converts fats into fatty acids and glycerol. This is referred to as emulsification of fats. It takes place in the small intestine.
Concept insight: Remember the various components of food and their digestion.
Solution 6
Saliva is secreted by salivary glands, located under the tongue. It moistens the food for easy swallowing. It contains a digestive enzyme called amylase, which breaks down starch into sugar.
Concept insight: Student should know the location and function of saliva.
Solution 7
Conditions necessary for autotrophic nutrition are:
(i) Carbon dioxide,
(ii) Water,
(iii) Chlorophyll pigment
(iv) Sunlight
Carbohydrates (food) and O2 are the by-products of photosynthesis.
Concept insight: Students should know the necessary conditions required for photosynthesis and the products formed during this process.
Solution 8
Differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration:
|
Aerobic respiration |
Anaerobic respiration |
|
i. Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of oxygen. ii. Complete breakdown of food occurs in aerobic respiration. iii. The end products in aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide and water. iv. Aerobic respiration produces a considerable amount of energy. |
i. Anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. ii. Partial breakdown of food occurs in anaerobic respiration. iii. The end products in anaerobic respiration may be ethanol and carbon dioxide (as in yeast plants), or lactic acid (as in animal muscles). iv. Much less energy is produced in anaerobic respiration. |
Yeast and bacteria uses anaerobic mode of nutrition.
Concept insight:
(i) Differences should always be written in tabular form.
(ii) Differences should be written in terms of their significance.
(iii) Write only those many numbers of differences as stated in the question.
(iv) Give example wherever possible.
Solution 9
The alveoli have a structure specialised for efficient gaseous exchange:
(i) Walls are extremely thin.
(ii)They have a large surface area in relation to volume.
(iii) They are surrounded by numerous blood capillaries.
Concept insight: Students should know the structure and function of alveoli.
Solution 10
Haemoglobin is the respiratory pigment that transports oxygen to the body cells for cellular respiration. Therefore, deficiency of haemoglobin in blood can affect its oxygen supplying capacity. This can lead to deficiency of oxygen in the body cells as a result of which the person suffers from anaemia, breathing problems and exhaustion.
Concept insight: Student should remember the components of blood and their respective functions.
Solution 11
A circulatory system in which the blood travels twice through the heart in one complete cycle of the body is called double circulation.
Solution 12
| Xylem | Phloem |
| i. Xylem conducts water and dissolved minerals from roots to leaves and other parts of the plant. | i. Phloem conducts prepared food materials from leaves to other parts of plant in dissolved form. |
| ii. In xylem, transport of materials take place through vessels and tracheids which are dead tissues. | ii. In phloem, transport of materials take place through sieve tubes with the help of companion cells, which are living cells. |
| iii. Movement of water and dissolved materials is also called ascent of sap. | iii. Transportation of food in plants is also called translocation of food. |
| iv. Movement of water is mainly achieved by transpiration pull and no energy is required. | iv. Translocation of food requires energy in the form of ATP. |
Concept insight:
(i) Differences should always be written in tabular form.
(ii) Differences should be written in terms of their significance.
(iii) Write only those many numbers of differences as stated in the question.
(iv) Give example wherever possible.
Solution 13
| Alveoli | Nephron |
| Struture | Structure |
| Alveoli are small sac-like structures present inside the lungs. | Nephrons are tubular structures present inside the kidneys. |
| The walls of the alveoli are one cell thick and it contains an extensive network of blood capillaries. | Nephrons are made of glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, and a long renal tube. It also contains a cluster of thin-walled blood capillaries. |
| Function | Function |
| Gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place in the alveoli. | Nephrons principal function is to control the absorption of water and soluble substances such as sodium salts by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is required and excreting the rest as urine. |
Concept insight:
(i) Differences should always be written in tabular form.
(ii) Differences should be written in terms of their significance.
(iii) Write only those many numbers of differences as stated in the question.
(iv) Give example wherever possible.
