Class 9 NCERT Solutions Maths Chapter 4: Linear Equations in Two Variables
Ex. 4.1
Ex. 4.2
Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 4.1
Solution 1
Let cost of notebook and a pen be x and y respectively.
Cost of note book = 2 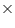 cost of pen
cost of pen
x = 2y
x - 2 y = 0
x = 2y
x - 2 y = 0
Solution 2
(i) 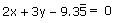
Comparing this equation with ax + by + c = 0
(ii) 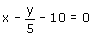
Comparing this equation with ax + by + c = 0
a = 1, b = - 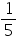 , c = -10
, c = -10
(iii) - 2x + 3 y = 6
- 2x + 3 y - 6 = 0
- 2x + 3 y - 6 = 0
Comparing this equation with ax + by + c = 0
a = - 2, b = 3, c = - 6
a = - 2, b = 3, c = - 6
(iv) x = 3y
1x - 3y + 0 = 0
Comparing this equation with ax + by + c = 0
a = 1, b = - 3, c = 0
1x - 3y + 0 = 0
Comparing this equation with ax + by + c = 0
a = 1, b = - 3, c = 0
(v) 2x = - 5y
2x + 5y + 0 = 0
2x + 5y + 0 = 0
Comparing this equation with ax + by + c = 0
a = 2, b = 5, c = 0
a = 2, b = 5, c = 0
(vi) 3x + 2 = 0
3x + 0.y + 2 = 0
3x + 0.y + 2 = 0
Comparing this equation with ax + by + c = 0
a = 3, b = 0, c = 2
a = 3, b = 0, c = 2
(vii) y - 2 = 0
0.x + 1.y - 2 = 0
0.x + 1.y - 2 = 0
Comparing this equation with ax + by + c = 0
a = 0, b = 1, c = - 2
a = 0, b = 1, c = - 2
(viii) 5 = 2x
- 2x + 0.y + 5 = 0
Company this equation with ax + by + c = 0
a = - 2, b = 0, c = 5
- 2x + 0.y + 5 = 0
Company this equation with ax + by + c = 0
a = - 2, b = 0, c = 5
Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise Ex. 4.2
Solution 1
y = 3x + 5 is a linear equation in two variables and it has infinite solutions. As for every value of x there will be a value of y satisfying above equation and vice versa.
Hence, the correct answer is (iii).
Hence, the correct answer is (iii).
Solution 2
(i) 2x + y = 7
For x = 0
2(0) + y = 7
For x = 0
2(0) + y = 7
So, (0, 7) is a solution of this equation
For x = 1
For x = 1
2(1) + y = 7
So, (1, 5) is a solution of this equation
For x = -1
2(-1) + y = 7
2(-1) + y = 7
So, (-1, 9) is a solution of this equation
For x = 2
2(2) + y = 7
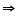 y = 3
y = 3
2(2) + y = 7
So (2, 3) is a solution of this equation.
(ii) 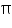
 + y = 9
+ y = 9
For x = 0
So (0, 9) is a solution of this equation
For x = 1
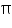 (1) + y =9
(1) + y =9
For x = 1
So, (1, 9 - 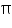 ) is a solution of this equation
) is a solution of this equation
For x = 2
So, (2, 9 -2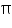 ) is a solution of this equation
) is a solution of this equation
For x = -1
y = 9 + 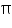
So, (-1, 9 + 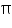 ) is a solution of this equation
) is a solution of this equation
(iii) x = 4y
For x = 0
0 = 4y
For x = 0
0 = 4y
So, (0, 0) is a solution of this equation
For y = 1
x = 4(1) = 4
So, (4, 1) is a solution of this equation
For y = - 1
x = 4(-1)
x = -4
So, (-4, - 1) is a solution of this equation
For x = 2
2 = 4y
For y = 1
x = 4(1) = 4
So, (4, 1) is a solution of this equation
For y = - 1
x = 4(-1)
x = -4
So, (-4, - 1) is a solution of this equation
For x = 2
2 = 4y
y = 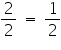
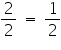
So,
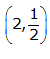 is a solution of this equation.
is a solution of this equation.Solution 3
(i) (0, 2)
Putting x = 0, and y = 2 in the L.H.S of given equation
x - 2y = 0 - (2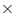 2 )
2 )
Putting x = 0, and y = 2 in the L.H.S of given equation
x - 2y = 0 - (2
= - 4
As -4 # 4
L.H.S # R.H.S
So (0, 2) is not a solution of this equation.
L.H.S # R.H.S
So (0, 2) is not a solution of this equation.
(ii) (2, 0)
Putting x = 2, and y = 0 in the L.H.S of given equation
x - 2y = 2 - (2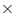 0)
0)
x - 2y = 2 - (2
= 2
As 2 # 4
L.H.S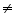 R.H.S
R.H.S
So (2, 0) is not a solution of this equation.
L.H.S
So (2, 0) is not a solution of this equation.
(iii) (4, 0)
Putting x = 4, and y = 0 in the L.H.S of given equation
x - 2y = 4 - 2(0)
= 4 = R.H.S
So (4, 0) is a solution of this equation.
Putting x = 4, and y = 0 in the L.H.S of given equation
x - 2y = 4 - 2(0)
= 4 = R.H.S
So (4, 0) is a solution of this equation.
(iv) 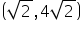
Putting x = 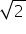 and y = 4
and y = 4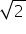 in the L.H.S of given equation.
in the L.H.S of given equation.
L.H.S
So
(v) (1, 1)
Putting x = 1, and y = 1 in the L.H.S of given equation
x - 2y = 1 - 2(1)
Putting x = 1, and y = 1 in the L.H.S of given equation
x - 2y = 1 - 2(1)
= 1 - 2
= - 1
As -1 # 4
L.H.S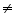 R.H.S
R.H.S
So (1, 1) is not a solution of this equation.
L.H.S
So (1, 1) is not a solution of this equation.
Solution 4
Putting x = 2, and y = 1 in the given equation
2x + 3y = k
2(2) + 3(1) = k
4 + 3 = k
k = 7
2(2) + 3(1) = k
4 + 3 = k
k = 7
