Class 9 NCERT Solutions Maths Chapter 7: Triangles
Ex. 7.1
Ex. 7.2
Ex. 7.3
Triangles Exercise Ex. 7.1
Solution 1
In 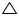 ABC and
ABC and 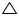 ABD
ABD
AC = AD (given)
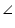 CAB =
CAB = 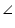 DAB (given)
DAB (given)
AB = AB (common)
AC = AD (given)
AB = AB (common)
So, BC and BD are of equal length.
Solution 2
In 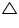 ABD and
ABD and 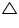 BAC
BAC
AD = BC (given)
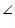 DAB =
DAB = 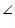 CBA (given)
CBA (given)
AB = BA (common)
AD = BC (given)
AB = BA (common)
And
Solution 3
In 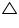 BOC and
BOC and 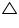 AOD
AOD
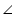 BOC =
BOC = 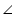 AOD (vertically opposite angles)
AOD (vertically opposite angles)
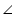 CBO =
CBO = 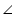 DAO (each 90o)
DAO (each 90o)
BC = AD (given)
BC = AD (given)

Solution 4

Solution 5

Solution 6
Given that 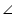 BAD =
BAD = 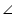 EAC
EAC
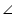 BAD +
BAD + 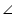 DAC =
DAC = 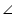 EAC +
EAC + 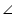 DAC
DAC
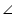 BAC =
BAC = 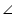 DAE
DAE
Now in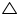 BAC and
BAC and 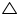 DAE
DAE
AB = AD (given)
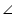 BAC =
BAC = 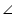 DAE (proved above)
DAE (proved above)
AC = AE (given)
Now in
AB = AD (given)
AC = AE (given)
Solution 7
Given that 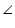 EPA =
EPA = 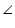 DPB
DPB
Now in
AP = BP (P is mid point of AB)
Solution 8
(i) In 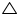 AMC and
AMC and 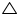 BMD
BMD
AM = BM (M is mid point of AB)
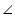 AMC =
AMC = 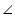 BMD (vertically opposite angles)
BMD (vertically opposite angles)
CM = DM (given)
AM = BM (M is mid point of AB)
CM = DM (given)
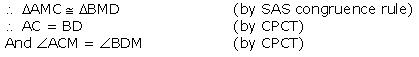
(ii) We have 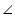 ACM =
ACM = 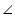 BDM
BDM
But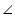 ACM and
ACM and 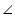 BDM are alternate interior angles
BDM are alternate interior angles
Since alternate angles are equal.
Hence, we can say that DB || AC
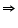
 DBC +
DBC + 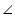 ACB = 180o (co-interior angles)
ACB = 180o (co-interior angles)  DBC + 90o = 180o
DBC + 90o = 180o
 DBC + 90o = 1800
DBC + 90o = 1800
But
Since alternate angles are equal.
Hence, we can say that DB || AC
(iii) Now in  DBC and
DBC and 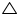 ACB
ACB
DB = AC (Already proved)
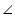 DBC =
DBC = 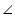 ACB (each 90o )
ACB (each 90o )
BC = CB (Common)
DB = AC (Already proved)
BC = CB (Common)
(iv) We have 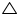 DBC
DBC 
 ACB
ACB

Triangles Exercise Ex. 7.2
Solution 1
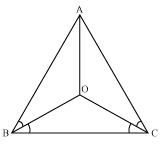
(i) It is given that in triangle ABC, AC = AB
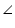 ACB =
ACB = 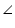 ABC (angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal)
ABC (angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal)
(ii) Now in 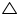 OAB and
OAB and  OAC
OAC
AO =AO (common)
AB = AC (given)
OB = OC (proved above)
So, OAB
OAB 
 OAC (by SSS congruence rule)
OAC (by SSS congruence rule)
AO =AO (common)
AB = AC (given)
OB = OC (proved above)
So,
Solution 2
In 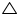 ADC and
ADC and 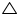 ADB
ADB
AD = AD (Common)
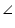 ADC =
ADC =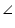 ADB (each 90o)
ADB (each 90o)
CD = BD (AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC)
AD = AD (Common)
CD = BD (AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC)
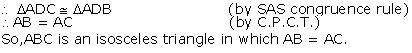
Solution 3
In 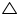 AEB and
AEB and 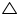 AFC
AFC
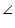 AEB =
AEB =  AFC (each 90o)
AFC (each 90o)
 A =
A =  A (common angle)
A (common angle)
AB = AC (given)
AB = AC (given)
Solution 4
(i) In  AEB and
AEB and 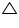 AFC
AFC
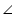 AEB =
AEB = 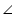 AFC (each 90)
AFC (each 90)
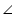 A =
A = 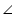 A (common angle)
A (common angle)
BE = CF (given)
BE = CF (given)
(ii) We have already proved
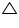 AEB
AEB 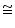
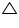 AFC
AFC
 AB = AC (by CPCT)
AB = AC (by CPCT)
Solution 5
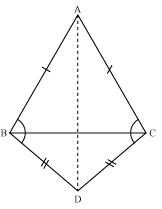
Let us join AD
In ABD and
ABD and  ACD
ACD
AB = AC (Given)
BD = CD (Given)
AD = AD (Common side)
In
AB = AC (Given)
BD = CD (Given)
AD = AD (Common side)
Solution 6
In  ABC
ABC
AB = AC (given)
 ACB =
ACB =  ABC (angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are also equal)
ABC (angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are also equal)
Now In ACD
ACD
AC = AD
 ADC =
ADC =  ACD (angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are also equal)
ACD (angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are also equal)
Now, in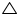 BCD
BCD
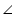 ABC +
ABC + 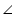 BCD +
BCD + 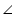 ADC = 180o (angle sum property of a triangle)
ADC = 180o (angle sum property of a triangle)
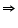
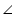 ACB +
ACB + 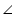 ACB +
ACB +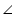 ACD +
ACD + 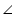 ACD = 180o
ACD = 180o
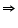 2(
2(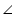 ACB +
ACB + 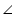 ACD) = 180o
ACD) = 180o
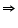 2(
2(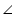 BCD) = 180o
BCD) = 180o
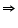
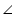 BCD = 90o
BCD = 90o
AB = AC (given)
Now In
AC = AD
Now, in
Solution 7
Given that
AB = AC
In  ABC,
ABC,
Solution 8
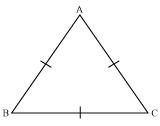
Let us consider that ABC is an equilateral triangle.
So, AB = BC = AC
Now, AB = AC
So, AB = BC = AC
Now, AB = AC
We also have
AC = BC
So, we have
Now, in
Hence, in an equilateral triangle all interior angles are of 60o.
Triangles Exercise Ex. 7.3
Solution 1
(i) In  ABD and
ABD and  ACD
ACD
AB = AC (given)
BD = CD (given)
AD = AD (common)
AB = AC (given)
BD = CD (given)
AD = AD (common)
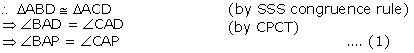
(ii) In  ABP and
ABP and  ACP
ACP
AB = AC (given).
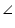 BAP =
BAP = 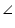 CAP [from equation (1)]
CAP [from equation (1)]
AP = AP (common)
AB = AC (given).
AP = AP (common)
(iii) From equation (1)
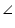 BAP =
BAP = 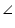 CAP
CAP
Hence, AP bisect A
A
Now in BDP and
BDP and  CDP
CDP
BD = CD (given)
DP = DP (common)
BP = CP [from equation (2)]
Hence, AP bisect
Now in
BD = CD (given)
DP = DP (common)
BP = CP [from equation (2)]
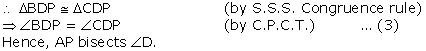
(iv) We have  BDP
BDP 
 CDP
CDP
Now, ![]() BPD +
BPD + ![]() CPD = 180o (linear pair angles)
CPD = 180o (linear pair angles)
![]() BPD +
BPD + ![]() BPD = 180o
BPD = 180o
2![]() BPD = 180o [from equation (4)]
BPD = 180o [from equation (4)]
![]() BPD = 90o ...(5)
BPD = 90o ...(5)
From equations (2) and (5), we can say that AP is perpendicular bisector of BC.
Solution 2
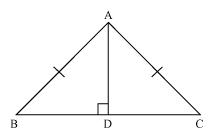
(i) In  BAD and
BAD and  CAD
CAD
 ADB =
ADB =  ADC (each 90o as AD is an altitude)
ADC (each 90o as AD is an altitude)
AB = AC (given)
AD = AD (common)
AB = AC (given)
AD = AD (common)

(ii) Also by CPCT,
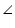 BAD =
BAD = 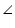 CAD
CAD
Hence, AD bisects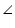 A.
A.
Hence, AD bisects
(ii) Also by CPCT,
ÐBAD = ÐCAD
Hence, AD bisects ÐA.
Solution 3
(i) In 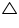 ABC, AM is median to BC
ABC, AM is median to BC
In  PQR, PN is median to QR
PQR, PN is median to QR
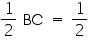 QR
QR But BC = QR
Now, in  ABM and
ABM and  PQN
PQN
AB = PQ (given)
BM = QN [from equation (1)]
AM = PN (given)
AB = PQ (given)
BM = QN [from equation (1)]
AM = PN (given)

(ii) Now in  ABC and
ABC and  PQR
PQR
AB = PQ (given)
BC = QR (given)
Solution 4
 In
In BC = CB (common)
BE = CF (given)
Hence, 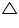 ABC is isosceles.
ABC is isosceles.
Solution 5
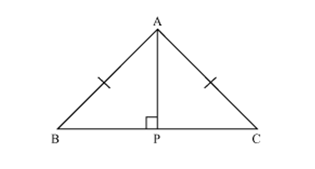
In  APB and
APB and  APC
APC
 APB =
APB = 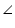 APC (each 90o)
APC (each 90o)
AB =AC (given)
AP = AP
AB =AC (given)
AP = AP
